Photosynthetic characterization and leaf anatomy of Chenopodium album and Ch. hircinum (Chenopodiaceae) in a high-altitude valley in Northwestern Argentina
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31055/1851.2372.v59.n1.42881Keywords:
Chenopodium, leaf anatomy, respiration, water use efficiencyAbstract
Background and aims: Chenopodium album (exotic) and Ch. hircinum (native) are weeds in different environments in Argentina. They tolerate various stress conditions so may have interesting traits for Ch. quinoa selection. This study aims to investigate the leaf anatomy and physiological photosynthetic behavior of former species to identify desirable traits for the improvement of quinoa.
M&M: Leaf morphological and physiological characteristics were evaluated in the targeted species growing spontaneously in a high mountain valley (1,995 m a.s.l.,Tucumán, Argentina).
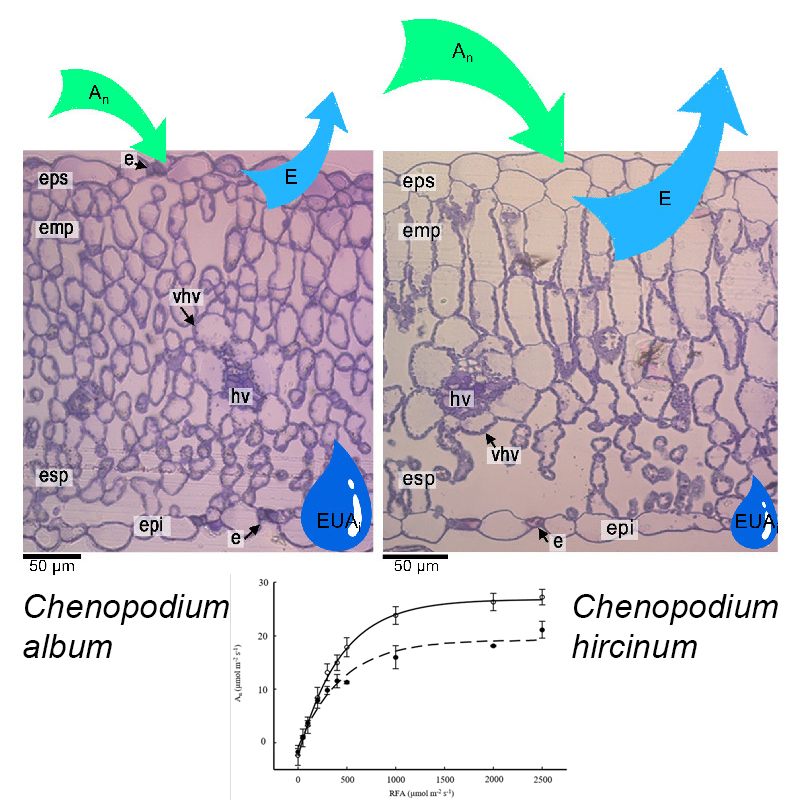
Results: Ch. hircinum exhibited higher net photosynthetic assimilation, stomatal conductance, internal CO2 concentration, nocturnal respiration, and light
compensation point. Ch. album showed higher concentrations of protective pigments and carotenoids, along with superior carboxylation capacity and intrinsic water use efficiency as well as a leaf blade with smaller isodiametric palisade mesophyll cells, higher percentage of intercellular air spaces and a greater density of bladder cells. These attributes allow Ch. album the capacity to survive in high mountain environments.
Conclusions: The attributes observed in both species provide valuable insights for targeted improvements in Ch. quinoa cultivation.
References
APN. Continuously updated. Sistema de Información de Biodiversidad de la Administración de Parques Nacionales, Argentina. Disponible en: https://sib.gob.ar/especies/chenopodium-album [Acceso: 28 septiembre 2023]
BAJWA, A. A., U. ZULFIQAR, S. SADIA, P. BHOWMIK & B. S. CHAUHAN. 2019. A global perspective on the biology, impact and management of Chenopodium album and Chenopodium murale: two troublesome agricultural and environmental weeds. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26: 5357-5371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-04104-y
BERTERO, H. D. & A. ALERCIA. 2016. Unravelling quinoa domestication with wild ancestors. En: MAXTED, N., M. E. DULLOO & B. V. FORD-LLOYD (eds.), Enhancing crop genepool use: capturing wild relative and landrace diversity for crop improvement, pp. 20-26. CABI Digital Library. https://doi.org/10.1079/9781780646138.0020
BERTOLINO, L. T., R. S. CAINE & J. E. GRAY. 2019. Impact of stomatal density and morphology on water-use efficiency in a changing world. Front. Plant Sci. 10: 225. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00225
BRUNO, M. C. & B. D. SMITH. 2006. A Morphological approach to documenting the domestication of Chenopodium in the Andes. En: ZEDER, M. A., D. BRADLEY, E. EMSHWILLER & B. D. SMITH (eds.), Documenting domestication: New genetic and archaeological paradigms, chapter 4, pp. 32-45. University of California Press, Berkeley. https://doi.org/10.1525/9780520932425-007
CAEMMERER, S. & J. EVANS. 1991. Determination of the average partial pressure of CO2 in chloroplasts from leaves of several C3 plants. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 18: 287-305. https://doi.org/10.1071/PP9910287
CHAPPELLE, E. W., M. S. KIM & J. E. MCMURTREY III. 1992. Ratio analysis of reflectance spectra (RARS): An algorithm for the remote estimation of the concentrations of chlorophyll A, chlorophyll B, and carotenoids in soybean leaves. Remote Sens. Environ. 39: 239-247. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-4257(92)90089-3
CHAVES-BARRANTES, N. F. & M. V. GUTIÉRREZ-SOTO. 2017. Respuestas al estrés por calor en los cultivos. II. Tolerancia y tratamiento agronómico. Agron. Mesoam. 28: 255-271. http://dx.doi.org/10.15517/am.v28i1.21904
CURTI, R. N., P. ORTEGA-BAES, J. SAJAMA, D. JARVIS, … & D. BERTERO. 2023. Exploration and collection of quinoa’s wild ancestor in Argentina. En: CHOUKR-ALLAH R. & R. RAGAB (eds.), Biosaline agriculture as a climate change adaptation for food security, pp. 167-178. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-24279-3_8
DIZEO DE STRITTMATTER, C. G. 1973. Nueva técnica de diafanización. Bol. Soc. Argent. Bot. 15: 126-129.
FAHN, A. & D. F. CUTLER. 1992. Xerophytes. Gebruder Borntraeger, Berlin.
FLEXAS, J., M. M. BARBOUR, O. BRENDEL, H. M. CABRERA, … & C. R. WARREN. 2012. Mesophyll diffusion conductance to CO2: An unappreciated central player in photosynthesis. Plant Sci. 193-194: 70-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2012.05.009
FRITZ, M. A., S. ROSA & A. SICARD. 2018. Mechanisms underlying the environmentally induced plasticity of leaf morphology. Front. Genet. 9: 478.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2018.00478
GEISSLER, N., S. HUSSIN, M. M. M. EL-FAR & H.-W. KOYRO. 2015. Elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration leads to different salt resistance mechanisms in a C3 (Chenopodium quinoa) and a C4 (Atriplex nummularia) halophyte. Environ. Exp. Bot. 118: 67-77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2015.06.003
GONZÁLEZ, J. A., M. BRUNO, M. VALOY & F. E. PRADO. 2010. Genotypic variation of gas exchange parameters and leaf stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes in ten quinoa cultivars grown under drought. J. Agron. Crop. Sci. 197, 81-93. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-037X.2010.00446.x
GONZÁLEZ, J. A., M. I. MERCADO, L. MARTINEZ-CALSINA, L. E. ERAZZÚ, … & G. I. PONESSA. 2022. Plant density effects on quinoa yield, leaf anatomy, ultrastructure and gas exchange. J. Agric. Sci. 160: 349-359. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859622000533
GUPTA, P. K. 2018. Veterinary toxicology. En: GUPTA, P. K. (ed.), Illustrated Toxicology, pp. 427-517. Academic Press, Cambridge. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813213-5.00015-8
HARAGUCHI, A., B. LI, S. MATSUKI, O. NAGATA & T. HARA. 2009. Variation and plasticity of photosynthesis and respiration in local populations of fat-hen Chenopodium album in northern Japan. Plant Species Biol. 24: 189-201. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-1984.2009.00254.x
HARRISON, E. L., L. ARCE CUBAS, J. E. GRAY & C. HEPWORTH. 2020. The influence of stomatal morphology and distribution on photosynthetic gas exchange. Plant J. 101: 768-779. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14560
HINOJOSA, L., J. GONZÁLEZ, F. BARRIOS-MASIAS, F. FUENTES & K. MURPHY. 2018. Quinoa abiotic stress responses: A review. Plants 7: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants7040106
KAPAZOGLOU, A., M. GERAKARI, E. LAZARIDI, K. KLEFTOGIANNI, E. SARRI, E. TANI, & P. J. BEBELI. 2023. Crop wild relatives: A valuable source of tolerance to various abiotic stresses. Plants 12: 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12020328
KUMAR, B., A. K. SINGH, R. N. BAHUGUNA, A. PAREEK & S. L.SINGLA‐PAREEK. 2023. Orphan crops: A genetic treasure trove for hunting stress tolerance genes. Food Energy Secur. 12: e436. https://doi.org/10.1002/fes3.436
LICHTENTHALER, H. K. 2007. Biosynthesis, accumulation and emission of carotenoids, α-tocopherol, plastoquinone, and isoprene in leaves under high photosynthetic irradiance. Photosynth Res. 92: 163-179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-007-9204-y
LUNDGREN, M. R., & A. J. FLEMING. 2020. Cellular perspectives for improving mesophyll conductance. The Plant J. 101: 845-857. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14656
MARENCO, R. A., J. F. DE C. GONCALVES & G. VIEIRA. 2001. Leaf gas exchange and carbohydrates in tropical trees differing in successional status in two light environments in central Amazonia. Tree Physiol. 21: 1311-1318. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/21.18.1311
MILTHORPE, F. L. & P. NEWTON. 1963. Studies on the expansion of the leaf surface: III. The influence of radiation on cell division and leaf expansion. J. Exp. Bot. 14: 483-495. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/14.3.483
MIRECKI, R. M. & A. H. TERAMURA. 1984. Effects of ultraviolet-B irradiance on soybean. Plant Physiol. 74: 475-480. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.74.3.475
MORIS, M., J. A. GONZÁLEZ, M. GALLARDO & F. E. PRADO. 1996. Anatomical and functional differences and nyctinastic leaf movements in Chenopodium album L. and Chenopodium hircinum Schrad. (Chenopodiaceae). Bot J Linn Soc. 121: 133-141. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8339.1996.tb00748.x
MUJICA, A. & S.-E. JACOBSEN. 2006. La quinua (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) y sus parientes silvestres. En: MORALES, M. R., B. ØLLGAARD, L. P. KVIST, F. BORCHSENIUS & H. BALSLEV (eds.), Botánica económica de los Andes Centrales, pp. 449-457. Universidad Mayor de San Andrés, La Paz.
MURPHY, K. M., J. B. MATANGUIHAN, F. F. FUENTES, L. R. GÓMEZ‐PANDO, … & D. E. JARVIS. 2018. Quinoa breeding and genomics. En: GOLDMAN, I. (ed.), Plant breeding reviews, pp. 257-320. Wiley, Oxford. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119521358.ch7
NISAR, N., L. LI, S. LU, N. C. KHIN & B. J. POGSON. 2015. Carotenoid metabolism in plants. Mol. Plant. 8: 68-82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2014.12.007
NOBEL, P. S., L. J. ZARAGOZA & W. K. SMITH. 1975. Relation between mesophyll surface area, photosynthetic rate, and illumination level during development for leaves of Plectranthus parviflorus Henckel. Plant Physiol. 55: 1067-1070. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.55.6.1067
OTTERBACH, S. L., H. KHOURY, T. RUPASINGHE, H. MENDIS, … & S. M. SCHMÖCKEL. 2021. Characterization of epidermal bladder cells in “Chenopodium quinoa”. Plant Cell Environ. 44: 3836-3852. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.14181
OZMEN, O., F. MOR, & A. UNSAL. 2003. Nitrate poisoning in cattle fed Chenopodium album hay. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 45: 83-84.
PALACIOS, M. B., A. J. RIZZO, T. B. HEREDIA, G. ROQUEIRO, …, & H. P. BURRIEZA. 2024. Structure, ultrastructure and cation accumulation in quinoa epidermal bladder cell complex under high saline stress. Protoplasma 2024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-023-01922-x
RAWSON, H. M., J. E. BEGG & R. G. WOODWARD. 1977. The effect of atmospheric humidity on photosynthesis, transpiration and water use efficiency of leaves of several plant species. Planta 134: 5-10. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390086
SCHULTE, M., C. OFFER & U. HANSEN. 2003. Induction of CO2-gas exchange and electron transport: comparison of dynamic and steady-state responses in Fagus sylvatica leaves. Trees 17: 153-163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-002-0219-x
SENASA. Continuously updated. Ministerio de Agricultura Ganadería, Pesca y Alimentos. Disponible en: http://www.senasa.gob.ar/normativas/disposicion-116-1964-ministerio-de-agricultura-ganaderia-pesca-y-alimentos [Accceso: 28 septiembre 2023]
SIMS, D. A. & R. W. PEARCY. 1992. Response of leaf anatomy and photosynthetic capacity in Alocasia macrorrhiza (Araceae) to a transfer from low to hagh light. Am. J. Bot. 79: 449-455. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1992.tb14573.x
SINGH, S., A. SINGH, S. S. HALLAN, A. BRANGULE, … & R. BHATIA. 2023. A compiled update on nutrition, phytochemicals, processing effects, analytical testing and health effects of Chenopodium album: a Non-Conventional Edible Plant (NCEP). Molecules 28: 4902. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28134902
SINGSAAS, E. L., D. R. ORT & E. H. DELUCIA. 2001. Variation in measured values of photosynthetic quantum yield in ecophysiological studies. Oecologia 128: 15-23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420000624
Sistema Nacional de Vigilancia y Monitoreo de Plagas. Continuously updated. Chenopodium album. Disponible en: https://www.sinavimo.gob.ar/plaga/chenopodium-album [Acceso: 29 septiembre 2023]
STEIBEL, P. E. 1986. Las Quenopodiaceas de la provincia de La Pampa. Rev. Fac. Agronomía (Univ. Nac. La Pampa) 2: 13-37.
THÉROUX-RANCOURT, G., A. B. RODDY, J. M. EARLES, M. E. GILBERT, … & C. R. BRODERSEN. 2021. Maximum CO2 diffusion inside leaves is limited by the scaling of cell size and genome size. Proc. R. Soc. B. 288: 20203145. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2020.3145
WELLBURN, A. R. 1994. The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J. Plant Physiol. 144: 307-313. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(11)81192-2
WRIGHT, I. J. & M. WESTOBY. 2002. Leaves at low versus high rainfall: coordination of structure, lifespan and physiology. New Phytol. 155: 403-416. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2002.00479.x
YORIMITSU, Y., A. KADOSONO, Y. HATAKEYAMA, T. YABIKU & O. UENO. 2019. Transition from C3 to proto-Kranz to C3–C4 intermediate type in the genus Chenopodium (Chenopodiaceae). J. Plant Res. 132: 839-855. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-019-01135-5
ZARLAVSKY, G. E. 2014. Histología vegetal: técnicas simples y complejas. Sociedad Argentina de Botánica, Buenos Aires.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Sebastian Edgardo Buedo, María I. Mercado, Juan A. González

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Provides immediate and free OPEN ACCESS to its content under the principle of making research freely available to the public, which fosters a greater exchange of global knowledge, allowing authors to maintain their copyright without restrictions.
Material published in Bol. Soc. Argent. Bot. is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International license.




