Evidences of population structure and spatial genetic structure at fine scale in Argentinean populations of Acacia furcatispina (Fabaceae)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31055/1851.2372.v54.n1.23587Keywords:
Acacia, AFLP, CDA, genetic structure, SGS, STRUCTURE.Abstract
Background and aims: Acacia furcatispina belongs to the subgenus Aculeiferum. Currently, there are no studies in population genetics in this species. The aim of this work was to investigate the genetic diversity, population structure and spatial genetic structure at fine scale (SGS) in Argentinean sample sites by means of molecular markers.
Materials and Metods: Two sample sites of A. furcatispina were studied with the AFLP technique. Three primer combinations were selected revealing for this study.
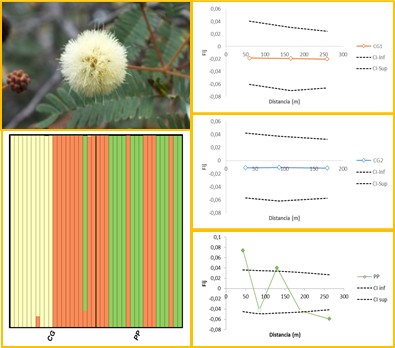
Results: The three primer combinations revealed a total of 121 AFLP bands. The percentage of polymorphic loci showed a mean value of 86.8 % and the mean heterozygocity was 0.33. The Bayesian analysis performed with software STRUCTURE detected three clusters (K= 3), corresponding one to Pasaje Pozo Zuni (PP) sample site and two for Cerro de la Gloria (CG) sample site, showing a subdivision of this last one (CG1 and CG2). The AMOVA showed that the great component of variability was represented within populations. The SGS detected significant structuration at short and middle distances in PP.
Conclusions: Based on the results of the present work, we recommend to sample trees far apart 10 m to minimize the kinship between individuals. These results present the first study in genetic diversity, population structure and spatial genetic structure at fine scale in A. furcatispina and all the analyses made here result of interest for management and conservation of this species.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Provides immediate and free OPEN ACCESS to its content under the principle of making research freely available to the public, which fosters a greater exchange of global knowledge, allowing authors to maintain their copyright without restrictions.
Material published in Bol. Soc. Argent. Bot. is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International license.




