Plant macroremains at Cueva Salamanca 1 archaeological site, Antofagasta de la Sierra (Catamarca, Argentine). Paleoenvironment and vegetation use during the Holocene
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31055/1851.2372.v54.n1.23586Keywords:
Archaeobotany, Holocene, hunter-gatherers, paleoenvironment, plant macroremains.Abstract
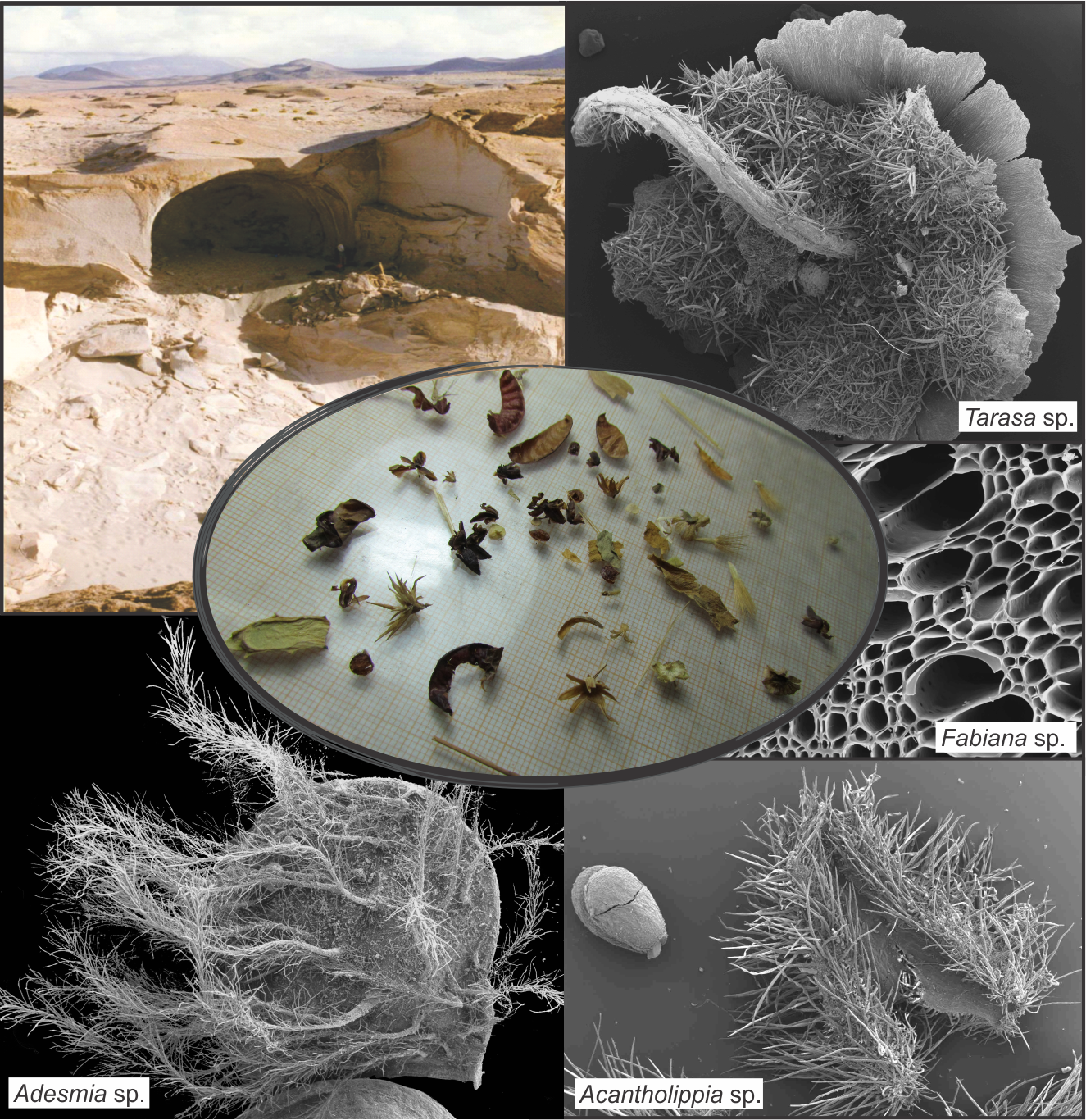
Background and aims: The archaeological site Cueva Salamanca 1 (CS1), Antofagasta de la Sierra (Catamarca, Argentina), is related to the grassland, tolar and lowland plant associations and was inhabited by hunter-gatherer groups (ca. 10,000 - 6,000 years BP). The plant remains recovered from the CS1 site are studied in order to determine the palaeoenvironmental conditions that occurred during the Holocene, which determined the use and specific exploitation of different plant associations by human groups that inhabited the site.
M&M: The plant macroremains recovered from CS1 were analysed with microscopy and by morphological comparisons with the species of the current flora surrounding the site.
Results: Of the 60 plant species that grow in the current environment related to the CS1 archaeological site, 44% are represented in the recovered, both herbaceous and woody charred and non-charred, belonging to the families Asteraceae, Brassicaceae, Cactaceae, Caryophyllaceae, Chenopodiaceae, Ephedraceae, Fabaceae, Malvaceae, Poaceae, Solanaceae and Verbenaceae. A greater use of the tolar is observed, followed by the grassland and the lowland during the whole sequence, considering the species that grow in a radius of 30 km from the site.
Conclusions: The human groups that inhabited CS1, during the Holocene Early Middle, Late Middle and Late, have made an effective occupation and knew and identified the different plant species to be exploited as fuel, preparation of manufactures and resting litters. The morphological and anatomical adaptations observed in the species found reflect the conditions of the paleoenvironment during the Holocene.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Provides immediate and free OPEN ACCESS to its content under the principle of making research freely available to the public, which fosters a greater exchange of global knowledge, allowing authors to maintain their copyright without restrictions.
Material published in Bol. Soc. Argent. Bot. is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International license.




