Variabilidad intraespecífica en el crecimiento y la producción in vitro de enzimas degradadoras de pared celular vegetal entre aislamientos argentinos de Colletotrichum graminicola, un patógeno de maíz
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31055/1851.2372.v58.n2.39049Palabras clave:
Antracnosis, Colletotrichum graminicola, Enzimas degradadoras de pared celular, MaízResumen
Introducción y objetivos: Colletotrichum graminicola (Glomerellaceae, Glomerellales) el agente causal de la antracnosis del maíz es dependiente de la actividad de enzimas degradadoras de la pared celular vegetal, para penetrar en su hospedante. La producción de estas enzimas se considera un factor de virulencia. El objetivo del presente trabajo fue investigar si existe variabilidad entre aislamientos en la capacidad de crecimiento y producción in vitro de diversas enzimas involucradas en la degradación de pared celular vegetal.
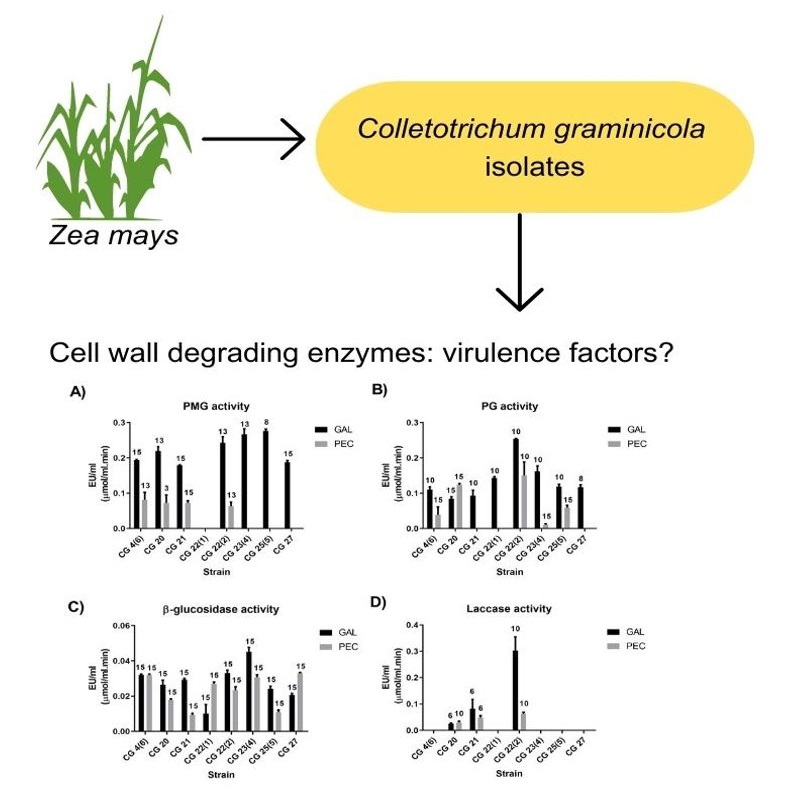
M&M: Se evaluó la habilidad de ocho aislamientos de C. graminícola para crecer y sintetizar enzimas con actividad poligalacturonasa, polimetilgalacturonasa, β-glucosidasa y lacasa en cultivos líquidos utilizando dos medios de diferente composición.
Resultados: La producción de poligalacturonasa, polimetilgalacturonasa y β-glucosidasa difirió marcadamente entre aislamientos y medios de cultivo. Se detectó actividad lacasa sólo en tres de los aislamientos. Los máximos títulos enzimáticos obtenidos fueron respectivamente de 250, 280, 45 y 63 U/l. La variabilidad intraespecífica registrada en la producción enzimática es consistente con la alta variabilidad intraespecífica observada a nivel genético cuando se evaluaron marcadores moleculares ISSR.
Conclusiones: Los aislamientos de C. graminicola investigados mostraron notables diferencias en cuanto a la producción de enzimas degradadoras de pared celular vegetal, no asociadas a su capacidad de crecimiento. Esto indica una importante variabilidad intraespecífica que debería tenerse en cuenta al seleccionar un método para combatir a este patógeno.
Referencias
ANDERSON, D. W. & R. L. NICHOLSON. 1996. Characterization of laccase in the conidial mucilage of Colletotrichum graminicola. Mycologia 88: 996-1002. https://doi.org/10.2307/3761063
ARMESTO, C., F. G. M. MAIA, F. P. MONTEIRO & M. S. ABREU. 2019. Exoenzymes as a pathogenicity factor for Colletotrichum gloeosporioides associated with coffee plants. Summa Phytopathol. 45: 368-373. https:// doi.org/10.1590/0100-5405/191071
BEBBER, D. P. & S. J. GURR. 2015. Crop-destroying fungal and oomycete pathogens challenge food security. Fungal Genet. Biol. 74: 62-64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2014.10.012
BELISÁRIO, R., A. E. ROBERTSON & L. J. VAILLANCOURT. 2022. Maize anthracnose stalk rot in the genomic era. Plant Dis. 106: 2281-2298. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-10-21-2147-FE
DA COSTA, R. V., L. V. COTA, D. D. DA SILVA, D. F. PARREIRA, C. R. CASELA, … & J. E. F. FIGUEIREDO. 2014. Races of Colletotrichum graminicola pathogenic to maize in Brazil. Crop Prot. 56: 44-49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2013.10.005
DEAN, R., J. A. L. VAN KAN, Z. A. PRETORIUS, K. E. HAMMOND-KOSACK, A. DI PIETRO, … & G. D. FOSTER. 2012. The top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 13: 414-430. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2011.00783.x
DE ROSSI, R., F. GUERRA, M. C. PLAZA, E. VULETIC, E. BRÜCHER, … & G. I. E. MAGNONE. 2016. Enfermedades del maíz en las últimas cinco campañas. In: Actas resúmenes 34° Congreso Aapresid “Resiliar”. Asociación Argentina de Productores en Siembra Directa, Rosario.
DÍAZ, C., R. DE ROSSI, L. COURETOT, M. SILLÓN, A. N. FORMENTO & V. GONZÁLEZ. 2012. Prevalencia y distribución de enfermedades del maíz en Argentina. In: Anais do 29° Congresso Nacional de Milho e Sorgo, pp. 26-30. Associação Brasileirea de Milho e Sorgo, São Paulo.
FERNÁNDEZ-VALIELA, M. V. 1979. Introducción a la Fitopatología. Vol IV. Hongos y Mycoplasmas. 3a Edición. Colección Científica INTA, Buenos Aires.
GALHAUP, C., H. WAGNER & B. HINTERSTOISSER. 2002. Increased production of laccase by the wood-degrading basidiomycete Trametes pubescens. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 30: 529-536.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(01)00522-1
GARCIA-MACEIRA, F. I., A. DI PIETRO & M. I. G. RONCERO. 2000. Cloning and disruption of pgx4 encoding an in planta expressed exopolygalacturonase from Fusarium oxysporum. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 13: 359-365. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI.2000.13.4.359
GATICA, S. M., M. GALLY, M. CARMONA, A. M. RAMOS & L. I. FERREYRA. 2014. Diferenciación genética de aislamientos de Colletotrichum graminicola de la región pampeana mediante marcadores ISSR. In: PLOPER, L. D. (ed.), Libro de Resúmenes del 3º Congreso Argentino de Fitopatología, pp. 511. Asociación Argentina de Fitopatólogos, Córdoba.
HAVE, A. T., W. MULDER, J. VISSER & J. A. VAN KAN. 1998. The endopolygalacturonase gene Bcpg1 is required for full virulence of Botrytis cinerea. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 11: 1009-1016.
https://doi.org/10.1094/mpmi.1998.11.10.1009
HUGOUVIEUX, V., S. CENTIS, C. LAFITTE & M. ESQUERRE-TUGAYE. 1997. Induction by (alpha)-L-arabinose and (alpha)-L-rhamnose of endopolygalacturonase gene expression in Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63: 2287-2292. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.63.6.2287-2292.1997
KIKOT, G. E., R. A. HOURS & T. M. ALCONADA. 2009. Contribution of cell wall degrading enzymes to pathogenesis of Fusarium graminearum: a review. J. Basic Microbiol. 49: 231-241.
https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.200800231.
KUBICEK C. P., T. L. STARR & N. L. GLASS. 2014. Plant cell wall-degrading enzymes and their secretion in plant-pathogenic fungi. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 52: 427-451.
https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-102313-045831
LEVIN, L., A. M. RAMOS, M. PARISI & M. GALLY. 2007. Screening of Colletotrichum (Ascomycota) isolates, causal agents of soybean anthracnose, for laccase production. Bol. Soc. Argent. Bot. 42: 71-77.
LIU, C. Q., K. D. HU, T. T. LI, Y. YANG, F. YANG, … & H. ZHANG. 2017. Polygalacturonase gene pgxB in Aspergillus niger is a virulence factor in apple fruit. PLoS One 12: e0173277.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0173277
LÓPEZ-PÉREZ, M., A. R. BALLESTER & L. GONZÁLEZ-CANDELAS. 2015. Identification and functional analysis of Penicillium digitatum genes putatively involved in virulence towards citrus fruit. Mol. Plant Pathol. 16: 262-275. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12179
MA, H., B. ZHANG, Y. GAI, X. SUN, K. R. CHUNG & H. LI. 2019. Cell-wall-degrading enzymes required for virulence in the host selective toxin-producing necrotroph Alternaria alternate of citrus. Front. Microbiol. 10: 2514. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02514
MÜNCH, S., U. LINGNER, D. S. FLOSS, N. LUDWIG, N. SAUER & H. B. DEISING. 2008. The hemibiotrophic lifestyle of Colletotrichum species. J. Plant Physiol. 165: 41-51.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2007.06.008
PACCANARO, M. C., L. SELLA, C. CASTIGLIONI, F. GIACOMELLO, A. L. MARTÍNEZ-ROCHA, … & F. FAVARON. 2017. Synergistic effect of different plant cell wall-degrading enzymes is important for virulence of Fusarium graminearum. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 30: 886-895. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-07-17-0179-R
PASZCZYNSKI, A. & R. L. CRAWFORD. 1991. Degradation of azo compounds by ligninase from Phanerochaete chrysosporium: Involvement of veratryl alcohol. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 178: 1056-1063. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291X(91)90999-N
RAMOS, A. M., M. GALLY, M. C. GARCÍA & L. LEVIN. 2010. Pectinolytic enzyme production by Colletotrichum truncatum, causal agent of soybean anthracnose. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 27: 186-190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.riam.2010.06.002.
RAMOS, A. M., M. GALLY, G. SZAPIRO, T. ITZCOVICH, M. CARABAJAL & L. LEVIN. 2016. In vitro growth and cell wall degrading enzyme production by Argentinean isolates of Macrophomina phaseolina, the causative agent of charcoal rot in corn. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 48: 267-273.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ram.2016.06.002
REIGNAULT, P., O. VALETTE-COLLET & M. BOCCARA. 2008. The importance of fungal pectinolytic enzymes in plant invasion, host adaptability and symptom type. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 120: 1-11.
https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s10658-007-9184-y
ROGERS, L. M., Y. K. KIM, W. GUO, L. GONZÁLEZ-CANDELAS, D. LI & P. E. KOLATTUKUDY. 2000. Requirement for either a host-or pectin-induced pectate lyase for infection of Pisum sativum by Nectria haematococca. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97: 9813-9818. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.160271497
SOMOGYI, M. J. 1952. Notes on sugar determination. Biol. Chem. 195: 19-23.
SUKNO, S. A., V. M. GARCÍA, B. D. SHAW & M. R. THON. 2008. Root infection and systemic colonization of maize by Colletotrichum graminicola. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74: 823-832.
https://doi.org/ 10.1128/AEM.01165-07
TEN HAVE, A., K. B. TENBERGE, J. A. E. BENEN, P. TUDZYNSKI, J. VISSER & J. A. L. VAN KAN. 2002. The contribution of cell wall degrading enzymes to pathogenesis of fungal plant pathogens. In: KEMPKEN, F. (ed.), The Mycota XI: Agricultural Applications, pp. 341-358. Springer, Heidelberg.
TORRES, M. F., N. GHAFFARI, E. A. BUIATE, N. MOORE, S. SCHWARTZ, … & L. J. VAILLANCOURT. 2016. A Colletotrichum graminicola mutant deficient in the establishment of biotrophy reveals early transcriptional events in the maize anthracnose disease interaction. BMC Genom. 17: 202. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-2546-0
VETCHINKINA, E., A. MESHCHEROV & V. GORSHKOV. 2022. Differential activity of the extracellular phenoloxidases in different isolates of the phytopathogenic fungus, Microdochium nivale. J. Fungi 8: 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/ jof8090918.
WANG, Y., J. WU, J. YAN, M. GUO, L. XU, … & Q. ZOU. 2022. Comparative genome analysis of plant ascomycete fungal pathogens with different lifestyles reveals distinctive virulence strategies. BMC Genom. 23: 34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-021-08165-1
WIJESUNDERA, R. L. C., J. A. BAILEY, R. J. W. BYRDE & A. H. FIELDING. 1989. Cell wall degrading enzymes of Colletotrichum lindemuthianum: their role in the development of bean anthracnose. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 34: 403-413. https://doi.org/10.1016/0885-5765(89)90067-2
WOOD, T. M. & K. M. BHAT. 1988. Methods for measuring cellulase activities. Methods Enzymol. 160: 87-112. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(88)60109-1
Descargas
Publicado
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2023 María del Pilar Nuñez, Laura Noemí Levin, Isabel Esther Cinto

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
El Bol. Soc. Argent. Bot.:
- Provee ACCESO ABIERTO y gratuito inmediato a su contenido bajo el principio de que hacer disponible gratuitamente la investigación al público, lo cual fomenta un mayor intercambio de conocimiento global.

- Permite a los autores mantener sus derechos de autor sin restricciones.
- El material publicado en Bol. Soc. Argent. Bot. se distribuye bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0 Internacional.






