Moringa oleifera (Moringaceae): leaf and stem anatomy and histochemistry
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31055/1851.2372.v54.n3.25357Keywords:
extrafloral nectary, histochemistry, leaf architecture, Moringa, morpho-anatomy, stem.Abstract
Background and aims: Moringa oleifera, is a tree grown in tropical and subtropical regions. Valorized for its multiple uses as ornamental, food, fodder, medicinal and industrial plant, it has been recently included in the Argentinean Food Code. The objective was to study the foliar and caulinar anatomy and histochemistry of M. oleifera specimens cultivated in Tucumán, Argentina in order to indicate diagnostic value characters for their identification.
M&M: The samples were analyzed under standard techniques for optical and electronic microscopy.
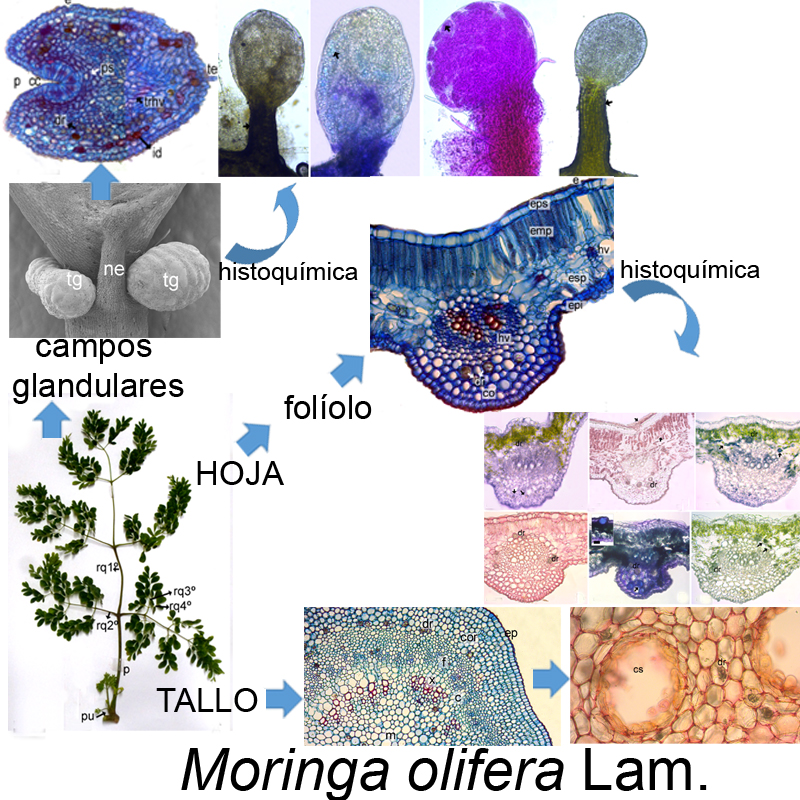
Results: M. oleifera presents pinnately compound leaves. Leaflets with pinnate, camptodromous-brochidodromous venation. Epicuticular waxes, eglandular trichomes; actinocytic and anomocytic stomata; dorsiventral mesophyll with proteins and lipids; collateral vascular bundles. Glandular fields formed by stipitate extrafloral nectaries, glandular trichomes and unicellular non-glandular trichomes. Petiolule, rachis and petiole with circular to sub-circular shape, vascular system formed by a solitary vascular bundle or a ring of collateral vascular bundles, surrounded by sclerenchyma. Medulla of the petiole with 1-2 secretory ducts containing proteins, alkaloids, mucilages and lipids. Stem with medulla with one or two secretory ducts, cortex with crystalline idioblasts (solitary calcium oxalate crystals). Idioblasts with phenols, tannins, saponins, triterpenes, polysaccharides and proteins were observed in leaf, petiole, rachis and stem.
Conclusions: The foliolar architecture, the presence of glandular fields, the histology of the nectaries, and the petiole; as well as the histochemistry of its aerial vegetative organs is described for the first time for M. oleifera. The characters of diagnostic value are: trichomes, glandular fields, extrafloral nectaries, idioblasts and secretory ducts.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Provides immediate and free OPEN ACCESS to its content under the principle of making research freely available to the public, which fosters a greater exchange of global knowledge, allowing authors to maintain their copyright without restrictions.
Material published in Bol. Soc. Argent. Bot. is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International license.








