Forensic anthropology, conservation and new technologies. Application of close-range photometry in human remains in Córdoba, Argentina
Main Article Content
Abstract
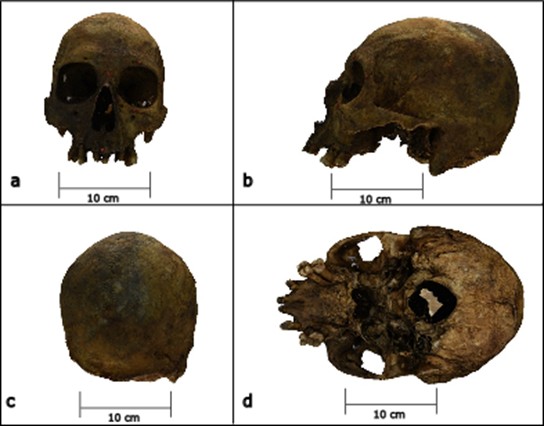
The objective of this work is to contribute to the discussion of the incorporation of new technologies to improve the conservation of human remains, from the implementation of short-range photogrammetry. The study was carried out on human skulls that are under the care of the Institute of Forensic Medicine of the Province of Córdoba, Argentina. Forensic Anthropology and short-range photogrammetry together make up an interdisciplinary field of study where our objective is focused on incorporating new documentation techniques for processing sensible remains and improving the conservation. The incorporation of a digital technique in the practice of this discipline allows us to propose an approach from another perspective to specific problems in this field, allowing the generation of new explanatory possibilities for issues that continually arise during the traditional work of forensic disciplines. In this sense, in the long term, we are interested in generating an information base that in the future will be transformed into a virtual repository with 3D records of human skulls of forensic, bioanthropological, historical and archaeological interest, and in the short term, optimizing the registration and conservation tasks of human remains through their three-dimensional digitization to be able to contribute to the identification and documentation tasks of judicial investigations that enter the institution. On the other hand, we are interested in discussing some ethical concepts focused on the growing digitization of human remains and the care that must be prioritized for their correct diffusion considering that at least in our country there is legislation that protects the exhibition of human remains.
Downloads
Article Details
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
COPYLEFT
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International License.
COPYRIGTH
The copyright and copyrights of the articles are held by the authors themselves.
This will be indicated in each article, as well as the Copyleft license described above.
How to Cite
References
AAPA
2003 Code of Ethics of the American Association of Physical Anthropologists. Approved by the AAPA Membership at the Annual Business Meeting on April 25, 2003. Retrieved from http://www.physanth.org/positions/ethics.htm
Aranda, C., G. Barrientos y M. Del Papa
2014 Código deontológico para el estudio, conservación y gestión de restos humanos de poblaciones del pasado. Revista Argentina de Antropología Biológica, 16(2), 111-113. Retrieved from https://revistas.unlp.edu.ar/raab/article/view/797
Balaguer Puig, M.
2018 Fotogrametría de Objeto Cercano: Conceptos básicos. Retrieved from https://m.riunet.upv.es
Boast, R. y P.F. Biehl
2011 Archaeological Knowledge Production and Dissemination in the Digital Age. In E. C. Kansa, S. W. Kansa, y E. Watrall (Eds.), Archaeology 2.0: New Approaches to Communication and Collaboration (pp. 119–156). Cotsen Institute of Archaeology Press at UCLA. https://doi.org/10.2307/j.ctvhhhfgw.15
Bowron, E.L.
2003 A New Approach to the Storage of Human Skeletal Remains. The Conservator 27(1) :95–106. https://doi.org/10.1080/01410096.2003.9995193
Buck U., S. Naether, B. Räss, C. Jackowski y M.J. Thali
2013 Accident or homicide -virtual crime scene reconstruction using 3D methods. Forensic Science International, 225(1-3), 75-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2012.05.015
Buikstra, J.E. y D. Ubelaker
1994 Standards for data collection from human skeletal remains. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajhb.1310070519
Caffell, A.C., C.A. Roberts, R.C. Janaway y A.S. Wilson
2001 Pressures on Osteological Collections: The Importance of Damage Limitation. En E. Williams (ed.) Human Remains: Conservation, Retrieval and Analysis: Proceedings of a Conference Held in Williamsburg, VA, Nov 7–11th 1999 (pp. 187–197). BAR International Series 934. Oxford: Archaeopress.
Carta de Londres
2009 La carta de Londres para la visualización computarizada del patrimonio cultural. Doi:10.4995/var.2011.4558
Charquero Ballester, A.M.
2016 Práctica y usos de la fotogrametría digital en arqueología. DAMA. Documentos de Arqueología y Patrimonio Histórico, 1, 139-157. http://dx.doi.org/10.14198/dama.2016.1.10
Charquero Ballester, A.M. y J.A. López Lillo
2012 Registro tridimensional acumulativo de la secuencia estratigráfica. Fotogrametría y SIG en la intervención arqueológica de lo Boligni (Alacant). Virtual Archaeology Review, 3(5), 81–88. https://doi.org/10.4995/var.2012.4529
Crowder, J.W., M. Fortun, R. Besara y L. Poirier (eds.)
2020 Anthropological Data in the Digital Age. New Possibilities – New Challenges. Palgrave Macmillan Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24925-0
Dueñas García, M.
2014 Registro arqueológico 3D mediante fotogrametría de rango corto. (Tesis de licenciatura). Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/335025734_Registro_arqueologico_en_3D_ mediante_la_fotogrametria_de_rango_corto
Endere, M.L. y P. Ayala
2012 Normativa legal, recaudos éticos y práctica arqueológica: un estudio comparativo Argentina y Chile. Chungará (Arica), 44(1), 39-57. https://dx.doi.org/10.4067/S0717-73562012000100004
Equipo Argentino de Antropología Forense
2005 EAAF Annual Report. Retrieved from https://eaaf.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/argentina_2005.pdf
2011 Informe antropológico forense sitio La Zanja Campo La Ribera. Inédito. Córdoba.
2021 Nuevas Tecnologías en Búsqueda Forense: Recursos para la crisis de desapariciones en México. Equipo Argentino de Antropología Forense (EAAF) y Centro de Derechos Humanos de las Mujeres (CEDEHM) (Eds.). Retrieved from https://eaaf.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/NUEVAS_TECNOLOGIAS_EN_BUSQUEDA_FORENSE-Recursos_para_la_crisis_de_desapariciones_en_Mexico_web.pdf
Evin A., T. Souter, A. Hulme-Beaman, C. Ameen, R. Allen, P. Viacava y K. Dobney
2016 The use of close-range photogrammetry in zooarchaeology: creating accurate 3D models of wolf crania to study dog domestication. Journal of Archaeological Sciences Reports, 9, 87-93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasrep.2016.06.028
Fau M., R. Cornette y A. Houssaye
2016 Photogrammetry for 3D digitizing bones of mounted skeletons: potential and limits. Comptes Rendus Palevol, 15(8), 968–977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crpv.2016.08.003
Ferreira, M.T., A.H. Ross y E. Cunha
2017 A reflection on the maintenance of identified skeletal collections state of preservation. La Revue de Médecine Légale, 8(4), 186. doi:10.1016/j.medleg.2017.10.01
Friess, M.
2012 Scratching the Surface? The use of surface scanning in physical and paleoanthropology. Journal of Anthropology Science, 90, 7-31. Doi: 10.4436/jass.90004
Ganiaris, H.
2001 London Bodies: An Exhibition at the Museum of London. En E. Williams (ed.) Human Remains: Conservation, Retrieval and Analysis: Proceedings of a Conference Held in Williamsburg, VA, Nov 7–11th 1999, (pp. 267–274). BAR International Series 934. Oxford: Archaeopress.
Garvin, H.M. y M.K. Stock
2016 The Utility of Advanced Imaging in Forensic Anthropology. Academic Forensic Pathology 6(3), 499-516. https://doi.org/10.23907/2016.050
González Ballesteros, J., J.G. Ángel, Gómez Carrasco, A. Hernández-Robles y J.A. Eiroa Rodríguez
2023 3D modelling of archaeological structures and deposits as a method of documentation and dissemination: the case of San Esteban Archaeological Site (Murcia, Spain). Virtual Archaeology Review, 14(29), 84–98. https://doi.org/10.4995/var.2023.18956
Guía Latinoamericana de buenas prácticas para la aplicación en Antropología Forense
2016 Retrieved from https://pdfcoffee.com/guia-latinoamericana-de-buenas-practicas-para-la-aplicacion-en-antropologia-forense-pdf-free.html
Hassett, Brenna R.
2018 The ethical challenge of digital bioarchaeological data. Archaeologies 14(2), 185–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11759-018-9348-8
Hirst, C. S., S. White y S.E. Smith
2018 Standardisation in 3D Geometric Morphometrics: Ethics, Ownership, and Methods. Archaeologies, 14(2), 1-27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11759-018-9349-7
Izaguirre, J. I.
2014 Nuevas Viejas Tecnologías. Modelos Tridimensionales aplicados al Noroeste argentino (Lic. Thesis, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Argentina). Retrieved from http://antropologia.filo.uba.ar/sites/antropologia.filo.uba.ar/files/documentos/TESIS% 20IZAGUIRRE%20final-.pdf
Katz D., y M. Friess
2014 3D from standard digital photography of human crania—a preliminary assessment. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 154(1),152-158. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajpa.22468
Kettner, M., P. Schmidt, S. Potente, F. Ramsthaler y M. Schrodt
2011 Reverse Engineering—Rapid Prototyping of the Skull in Forensic Trauma Analysis. Journal of Forensic Sciences, 56(4), 1015-1017. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1556-4029.2011.01764.x
Lauria, G., L. Sineo y S. Ficarra
2022 A detailed method for creating digital 3D models of human crania: an example of close‐range photogrammetry based on the use of Structure‐from‐Motion (SfM) in virtual anthropology. Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, 14(42). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12520-022-01502-9
Lorenzo G., L. Lopez, R.A. Moralejo y L.M. del Papa
2019 SfM photogrammetry applied to taxonomic determination of archaeofauna remains. Virtual Archaeological Review, 10(20), 70-83. https://doi.org/10.4995/var.2019.11094
Lowe, D. G.
1999 Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, 2(1), 1150–1157. Doi:10.1109/ICCV.1999.790410.
Luhman, T., Robson, T., Kyle, Stephen., y Boehm, J. (2014). Close-Range Photogrammetry and 3D Imaging. Berlin: De Gruyter.
Lussu, P. y E. Marini
2020 Ultra close-range digital photogrammetry in skeletal anthropology: A systematic review. PLOS ONE, 15(4), 1-29. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0230948
Márquez-Grant, N., y D. Errickson
2017 Ethical considerations: An added dimension. In Human Remains: Another Dimension: The Application of Imaging to the Study of Human Remains. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-804602-9.00015-1
Morgan B., A.L. Ford y M.J. Smith
2019 Standard methods for creating digital skeletal models using structure-from-motion photogrammetry. American Journal of Physical Anthropology 169(1),152-160. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajpa.23803
Nyimbili, P. H., H. Demirel, D.Z. Şeker y T. Erden
2016 Structure from Motion (SfM) - Approaches and Applications. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/327630010_Structure_from_Motion_SfM_- _Approaches_and_Applications
Olmo, D. (comp)
2005 Equipo Argentino de Antropología Forense. Cementerio de San Vicente Informe 2003. Ferreyra Editor, Córdoba.
Olmo, D. y M. Salado Puerto
2008 Una fosa común en el interior de Argentina: el Cementerio de San Vicente. Revista del Museo de Antropología, 1(1) 3-12. https://doi.org/10.31048/1852.4826.v1.n0.5390
Omari, R., C. Hunt, J. Coumbaros y B. Chapman
2021 Virtual anthropology? Reliability of three-dimensional photogrammetry as a forensic anthropology measurement and documentation technique. International Journal of Legal Medicine, 135, 939–950. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-020-02473-z
Principios de Sevilla
2001 Retrieved from http://www.arqueologiavirtual.com/carta/wp-content/uploads/2012/03/BORRADOR- FINAL-FINAL-DRAFT.pdf
Profico, A., L. Bellucci, C. Buzi, F. Di Vincenzo, I. Micarelli, F. Strani y G. Manzi
2018 Virtual Anthropology and its Application in Cultural Heritage Studies. Studies in Conservation, 1(1),1–14. Doi: 10.1080/00393630.2018.1507705
Ramírez, D., H. Saka y R. Nores
2021 Detection of Vibrio cholerae aDNA in human burials from the fifth cholera pandemic in Argentina (1886–1887 AD). International Journal of Paleopathology, 32, 74-79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpp.2020.12.004
Randolph-Quinney, P. S., S.D. Haines y A. Kruger
2018 The Use of Three-Dimensional Scanning and Surface Capture Methods in Recording Forensic Taphonomic Traces: Issues of Technology, Visualization, and Validation. In P. M. Barone, y M. J. W. Groen. (Eds.), Multidisciplinary Approaches to Forensic Archaeology (pp. 115-130). New York: Springer.
Redman, C.L.
1987 Surface collection, sampling, and research design: a retrospective. American Antiquity, 52(2) 249-265. https://doi.org/10.2307/281779
Sangripanti, G., D. Villalba, D. Aguilera y A. Giaccardi
2013 Geología forense: métodos aplicados en la búsqueda de desaparecidos en la región central de Argentina. Revista de la Asociación Geológica Argentina, 70(1), 150-160. https://revista.geologica.org.ar/raga/article/view/499
Santos, D., P. Dias, D. Souza, H. Santos, C. Coelho, M.T. Ferreira, E. Cunha y B. Sousa Santos
2013 Um novo método de medições craniométricas usando modelos 3D. Conference: Information Visualisation (IV), 2013 17th International Conference. Doi: 10.1109/IV.2013.61
Sardi, M. L., M.M. Reca y H.M. Pucciarelli
2015 Debates y decisiones políticas en torno de la exhibición de restos humanos en el Museo de La Plata / Debates and political decisions on the exhibition of human remains in the Museum of La Plata. Revista Argentina De Antropología Biológica, 17(2), 1-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.17139/raab.2015.0017.02.04.
Schug, G., K. Killgrove, A. Atkins, y K. Baron
2021 3D Dead. Ethical Considerations in Digital Human Osteology. Bioarchaeology International, 4(3–4), 217–230. https://doi.org/10.5744/bi.2020.3008
Serrano-Ramos, A.
2022 Crania Canaria 2.0: constructing a virtual skull collection. Virtual Archaeology Review, 13(26), 76–87. https://doi.org/10.4995/var.2022.16082
Squires, K. y R.G. Mancuso
2021 Desafíos éticos asociados al estudio y tratamiento de restos humanos en las ciencias antropológicas en el siglo XXI. Revista Argentina De Antropología Biológica, 23(2), 1-34. https://doi.org/10.24215/18536387e034
Ulguim, P.F.
2017 Recording in situ human remains in three dimensions: applying digital image-based modeling. In D. Errickson., y T. Thomson. (Eds.), Humans Remains: Another Dimension (pp. 71-92). London: Academic Press.
Uribe, A.
2011 “Informe de trabajo de investigación arqueológica en el Sitio La Zanja, Campo La Ribera. Inédito. Córdoba.
Vega, P.
2021 Córdoba en tiempos de cólera. Análisis bioarqueológico de la epidemia de 1886/87. (Lic Thesis, Universidad de Córdoba, Argentina).
Weber, G.W. y F.L. Bookstein
2011 Virtual Anthropology: A Guide to a New Interdisciplinary Field. Vienna: Springer.
White, S., C. Hirst y S.E. Smith
2018 The suitability of 3D data: 3D digitisation of human remains. Archaeologies 14(2), 250-271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11759-018-9347-9
White S. y S.E. Smith
2018 Standardisation in 3D geometric morphometrics: ethics, ownership, and methods. Archaeologies 14(2), 272-298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11759-018-9349-7
Wrobel, G. D., J.A. Biggs y A.L. Hair
2019 Digital Modelling for Bioarchaeologist. Advances in Archaeological Practice, 7(1), 47-54. Doi: 10.1107/aap2018.47